CANNY 7.2 Duo. CAN Gateway Driver
General Description
Using the CAN gateway driver you can implement high-speed asynchronous relaying of messages between CAN hardware interfaces with optional filtering and alteration of specific CAN messages.
The CAN gateway driver allows you to set up individual processing of incoming CAN messages by configuring up to 18 selection rules (selectors).
Each rule (selector) enables you to select CAN messages by the combination of the following user-defined properties:
- CAN interface number through which the message was coming to the controller;
- CAN ID of incoming message (CAN gateway selector value);
- length of incoming message (CAN gateway selector value);
- any combination of the 8 data byte (D0..D7) values of the message, including values of individual bits(CAN gateway selector value).
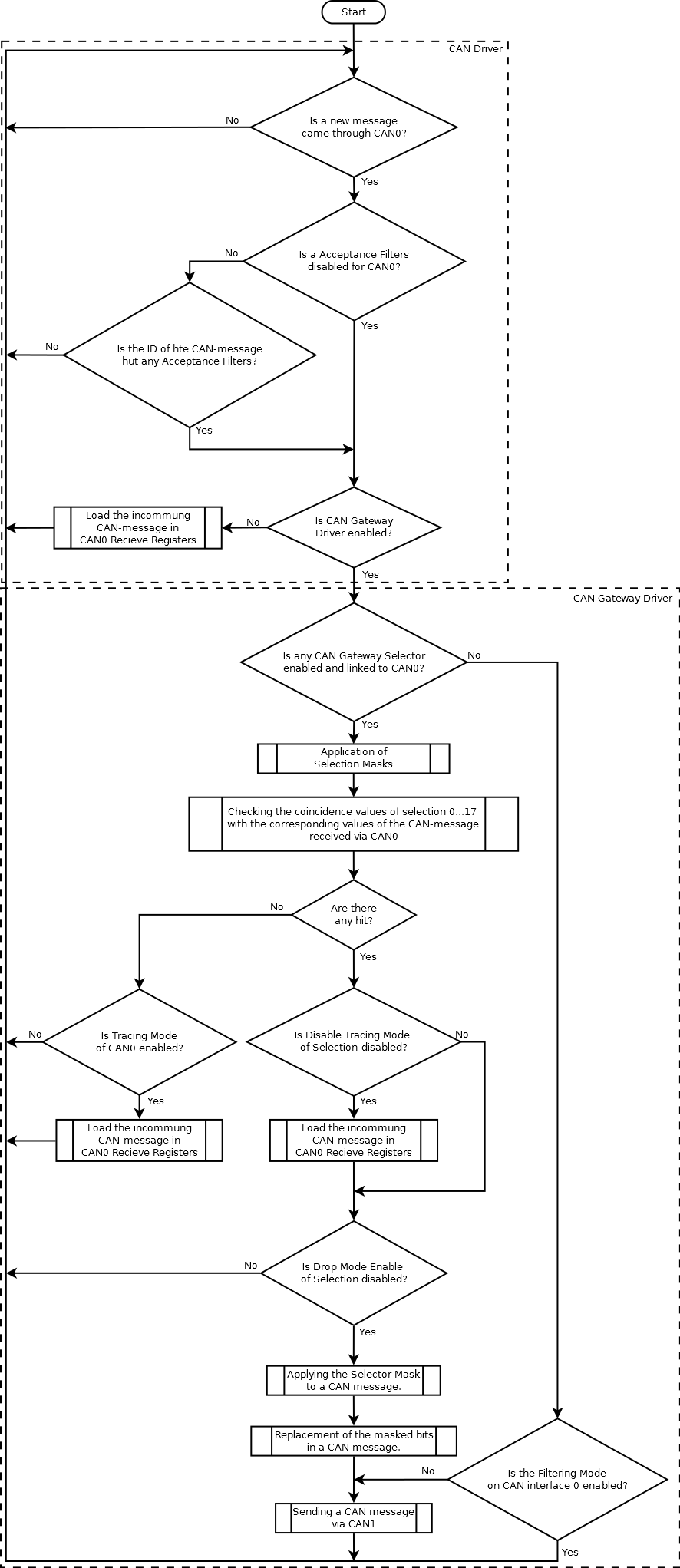
When an incoming CAN message hit the selector, the CAN gateway driver performs one of the following user-defined actions:
- relay the message to another CAN interface of the controller “as is”, without any changes;
- modify the message and then relay the modified message to another CAN interface of the controller;
- discard the message.
Message modification it is performed by replacement of any bits of the original message using a bitmask. You can change any CAN-message field including ID, length and bits of data.
For all incoming CAN messages coming through a certain CAN interface that are do not hit any selector rules, you can assign one of the following actions:
- relay the message to another CAN interface of the controller “as is”, without any changes;
- discard the message.
To use the CAN gateway driver, you need to specify driver configurations for both CAN interfaces of the controller. Each interface can have different configuration values.
When the CAN gateway driver is enabled, the diagram can still use the registers of the CAN0 Driver and the CAN1 Driver to:
- send CAN messages through any of the CAN interfaces;
- receive CAN messages that hit some CAN gateway driver selector rule of the CAN interface.
Moreover, you can change CAN gateway driver configuration values during operation from the function diagram. This lets you implement a dynamic mode for your CAN gateway.
Drivers registers
Below is a description of CAN gate driver control registers. These registers set the controller operation parameters for high-speed asynchronous relaying of messages between the CAN hardware interfaces.
| Register | Expected values |
|---|---|
| CAN Gateway Driver Enable Register | ≥ 1 = enable the CAN Gateway Driver; 0 = disable the CAN Gateway Driver. |
| CAN Gateway Configuration Update Register | ≥ 1 = apply new settings of the CAN gateway driver. Must be set momentarily when the CAN Gateway Driver parameters need be changed during function diagram execution; 0 = do not update the settings of the CAN gateway driver. |
| CAN Gateway Filtering Mode on CAN interface X | ≥ 1 = switch on the filtering mode of the CAN gateway for the specified interface: only relay messages to the second CAN interface of the controller and transmit them to the function diagram (CANx driver) if they are accepted by the gateway selections. Discard the remaining messages; 0 = the filtering mode of the CAN gateway for the specified interface is disabled: automatically retransmit messages that have not been accepted by the gateway selections to the second CAN-interface of the controller in unmodified form. |
| CAN Gateway Tracing Mode on CAN interface X | ≥ 1 = enable the CAN gateway tracing mode for the specified interface: transmit all CAN messages received on this interface to the function diagram (the CANx driver). The gateway driver will still select, replace and relay CAN messages according to the gateway settings of the specified CAN interface; 0 = disable the CAN gateway tracing mode for the specified interface: only CAN messages that are included in the gateway’s selections are transmitted to the diagram (to the CANx driver), the remaining messages are discarded. |
Note: New gateway driver settings will be applied on the diagram loop that follows the loop during which a non-zero value was written to the CAN Gateway Configuration Update Register.
| Register | Expected values |
|---|---|
| CAN Gateway Overflow Register | 1 = error, CAN Gateway Driver overflow occurred (see note); 0 = no CAN Gateway Driver overflow detected, the driver is operating normally. |
| CAN Gateway CANx Interface Selector Hit Register | 0…17 = selector number to which the currently (latest) received CAN message on the specified interface corresponds. |
Note: The occurrence of an overflow error in the CAN Gateway Driver means that by the time a new CAN message arrives, the previous message from the same selection has not yet been read and processed. The previous message has been overwritten with a newer one and data loss has occurred.
| Register | Expected values |
|---|---|
| CAN Gateway Selector X Enable Register | ≥ 1 = enable the appropriate selector of the CAN gateway; 0 = the corresponding CAN gateway selector is disabled. |
| CANGW Selector X Linked CAN Interface Number Register | 0 = apply the appropriate selector to messages coming to the controller via the CAN0 interface; 1 = apply the appropriate selector to messages coming to the controller via the CAN1 interface. |
| CAN Gateway Selector X Drop Mode Enable Register | ≥ 1 = discard all messages which match the enabled selector; 0 = allow processing and automatic retransmission to another CAN interface of all messages that match the enabled selector. |
| CAN Gateway Selector X Disable Tracing Register | ≥ 1 = disable the transfer of corresponding selection data to CAN driver registers, make the selected messages inaccessible in the user diagram; 0 = enable the transfer of the corresponding selection data to the CAN driver registers, make the selected messages accessible in the user diagram. |
The value of the selection - is a parameter which, when satisfied, selects an incoming CAN message for special processing.
| Register | Expected values |
|---|---|
| CAN Gateway Selector X Value Setup Register, CAN IDL | 0…0xFFFF = value of the lower part of the identifier (bits 0 … 10 for the standard format identifier or bits 0 … 15 for the extended format identifier) of the CAN message the selection will accept. |
| CAN Gateway Selector X Value Setup Register, CAN IDH | 0…0x1FFF = value of the upper part of the identifier (bits 16 … 28 for the extended format identifier) of the CAN message the selection will accept. |
| CAN Gateway Selector X Value Setup Register, CAN ERL | 0…0xXX08 = value equal to the number of data bytes in the received CAN message on the specified interface, where 0xXX is: 0x00 (with standard format), 0x40 (with standard format with RTR), 0x80 (with extended format) or 0xС0 (with extended format with RTR) (See note). |
| CAN Gateway Selector X Value Setup Register, CAN D1:D0 … CAN Gateway Selector X Value Setup Register, CAN D1:D0 |
0…0xFFFF = data byte values of CAN message data, according to which a check is made for compliance of the message with this selection. |
Note: CAN Gateway Selector X Value Setup Register CAN ERL denotes the number of bytes in the received message in its least significant bits (bits 0..8). It also contains information about special message attributes in its most significant bits : bit 15 - EXT flag, bit 14 - RTR flag. EXT = 1, when a message is received in the extended format, EXT = 0 for the standard message format; RTR = 1 when a remote data request is received, RTR = 0 when a normal message is received.
Note: To work with extended identifiers, the most significant bit (bit 15 - EXT mark) of the “CAN Gateway Selector X Value Setup Register, CAN ERL” must be set equal to 1. Accordingly, in the “CAN Gateway Selector X Mask Setup Register, CAN ERL”, bit 15 must also be set equal to 1.
The selection masks is a group of values, whose bits define the parts of incoming messages that are bitwise compared to corresponding selector values. When the mask bit value is 0, the corresponding message bit value is ignored, meaning that it has no impact on whether or not the message hits the selector. If the mask bit value is 1, the message bit will be compared to the corresponding Selector Value bit. If all incoming message bit values, as defined by the selection masks, are equal to their corresponding Selector Value bits, then the message is selected for further processing.
| Register | Expected values |
|---|---|
| CAN Gateway Selector X Mask Setup Register, CAN IDL | 0…0xFFFF = set mask value of the lower part of the CAN message identifier (bits 0 … 10 of the standard format identifier or bits 0 … 15 of the extended format identifier) of the corresponding selection. |
| CAN Gateway Selector X Mask Setup Register, CAN IDH | 0…0x1FFF = set mask value of the upper part of the CAN message identifier (bits 16 … 28 of the extended format identifier) of the appropriate selection. |
| CAN Gateway Selector X Mask Setup Register, CAN ERL | 0…0xFFFF = set mask value of the ERL register of the CAN message of the appropriate selection. |
| CAN Gateway Selector X Mask Setup Register, CAN D1:D0 … CAN Gateway Selector X Mask Setup Register, CAN D7:D6 |
0…0xFFFF = set mask for the corresponding byte of data of the CAN message of the corresponding selection. |
Selector replacement mask is a group of values, whose bits define the parts of incoming messages that will be modified when the gateway relays the selected message. When the mask bit value is 0, the corresponding bit of the incomind message will be relayed to the other CAN interace unmodified. If the mask bit valaue is 1, the bit will be replaced by the corresponding bit from the selector’s replace value registers.
| Register | Expected values |
|---|---|
| CAN Gateway Selector X Replace Mask Setup Register, CAN IDL | 0…0xFFFF = set replacement mask value of the lower part of the CAN message identifier (bits 0 … 10 of the standard format identifier or bits 0 … 15 of the extended format identifier) of the corresponding selection. |
| CAN Gateway Selector X Replace Mask Setup Register, CAN IDH | 0…0x1FFF = set replacement mask value of the upper part of the CAN message identifier (bits 16 … 28 of the extended format identifier) of the appropriate selection. |
| CAN Gateway Selector X Replace Mask Setup Register, CAN ERL | 0…0xFFFF = set replacement mask value of the ERL register of the CAN message of the appropriate selection. |
| CAN Gateway Selector X Replace Mask Setup Register, CAN D1:D0 … CAN Gateway Selector X Replace Mask Setup Register, CAN D7:D6 |
0…0xFFFF = set replacement mask for the corresponding byte of data of the CAN message of the corresponding selection. |
Replacement of selection - is a group of values whose bits replace the original bits in the relayed message that has been selected. If the value of the replacement bit is “0”, the corresponding bit of the relayed message will be replaced by a zero, with the replacement bit value equal to “1”, the corresponding bit of the relayed message will be replaced by 1. The replacement will only be applied to those bits whose selection mask value is “1”.
| Register | Expected values |
|---|---|
| CAN Gateway Selector X Replace Setup Register, CAN IDL | 0…0xFFFF = replacement value of the lower part of the CAN message identifier (bits 0 … 10 of the standard format identifier or bits 0 … 15 of the extended format identifier) of the corresponding selection. |
| CAN Gateway Selector X Replace Setup Register, CAN IDH | 0…0x1FFF = replacement value of the highest part of the CAN message identifier (bits 16 … 28 of the extended format identifier) of the corresponding selection. |
| CAN Gateway Selector X Replace Setup Register, CAN ERL | 0…0xFFFF = replacement value of the ERL register of the CAN message of the selection being used. |
| CAN Gateway Selector X Replace Setup Register, CAN D1:D0 … CAN Gateway Selector X Replace Setup Register, CAN D7:D6 |
0…0xFFFF = replacement values of the corresponding data bytes of the CAN message of the corresponding selection. |
CAN Gateway Driver operation diagram
Examples
Disable the retransmission of CAN messages with the specified identifier
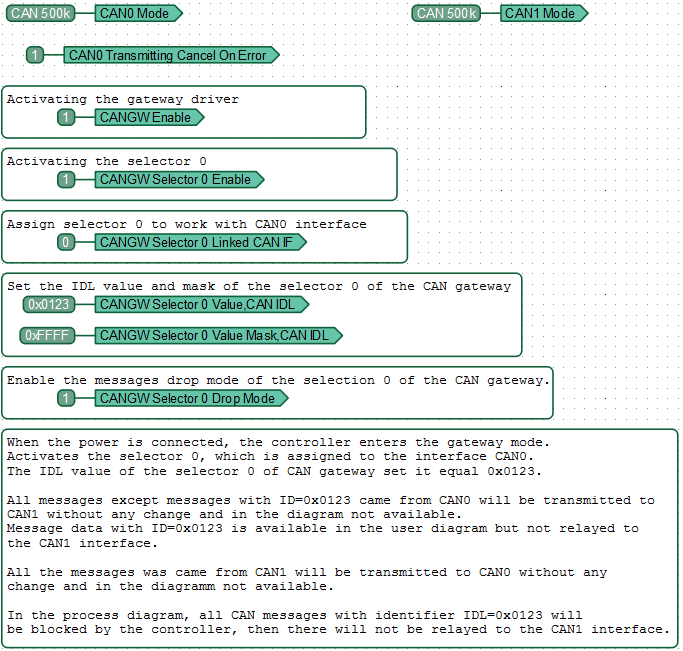
All messages that come from CAN0, except messages with ID = 0x0123, are transmitted to the CAN bus without any changes and are not transmitted to the function diagram (CAN driver). Data of messages with ID = 0x0123 is available to the function diagram, but not relayed to the CAN1 interface.
All messages coming from CAN1 are transmitted to CAN0 without changes and not included in the diagram.
Static Gateway: modify CAN message data and relay the modified messages
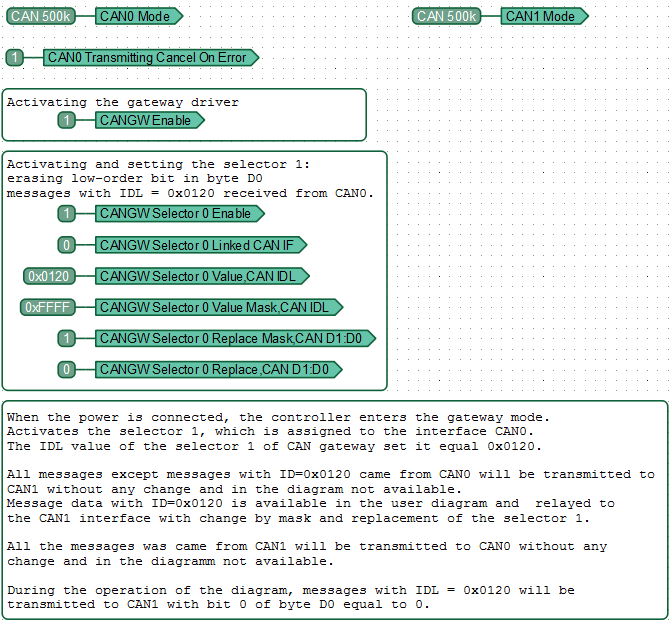
All messages, except messages with ID = 0x0120, that come from CAN0 are transmitted to CAN1 without any changes and are not included in the diagram. Data of messages with ID = 0x0120 is available in the user diagram. These messages are also relayed to the CAN1 interface after undergoing a bitwise replacement procedure.
All messages coming from CAN1 are transmitted to CAN0 without any changes, and are not included in the diagram.
In the process of diagram execution, messages with IDL = 0x0120 will be transmitted to CAN1 with a bit of 0 byte D0 equal to 0.
Processing received CAN messages in a custom diagram
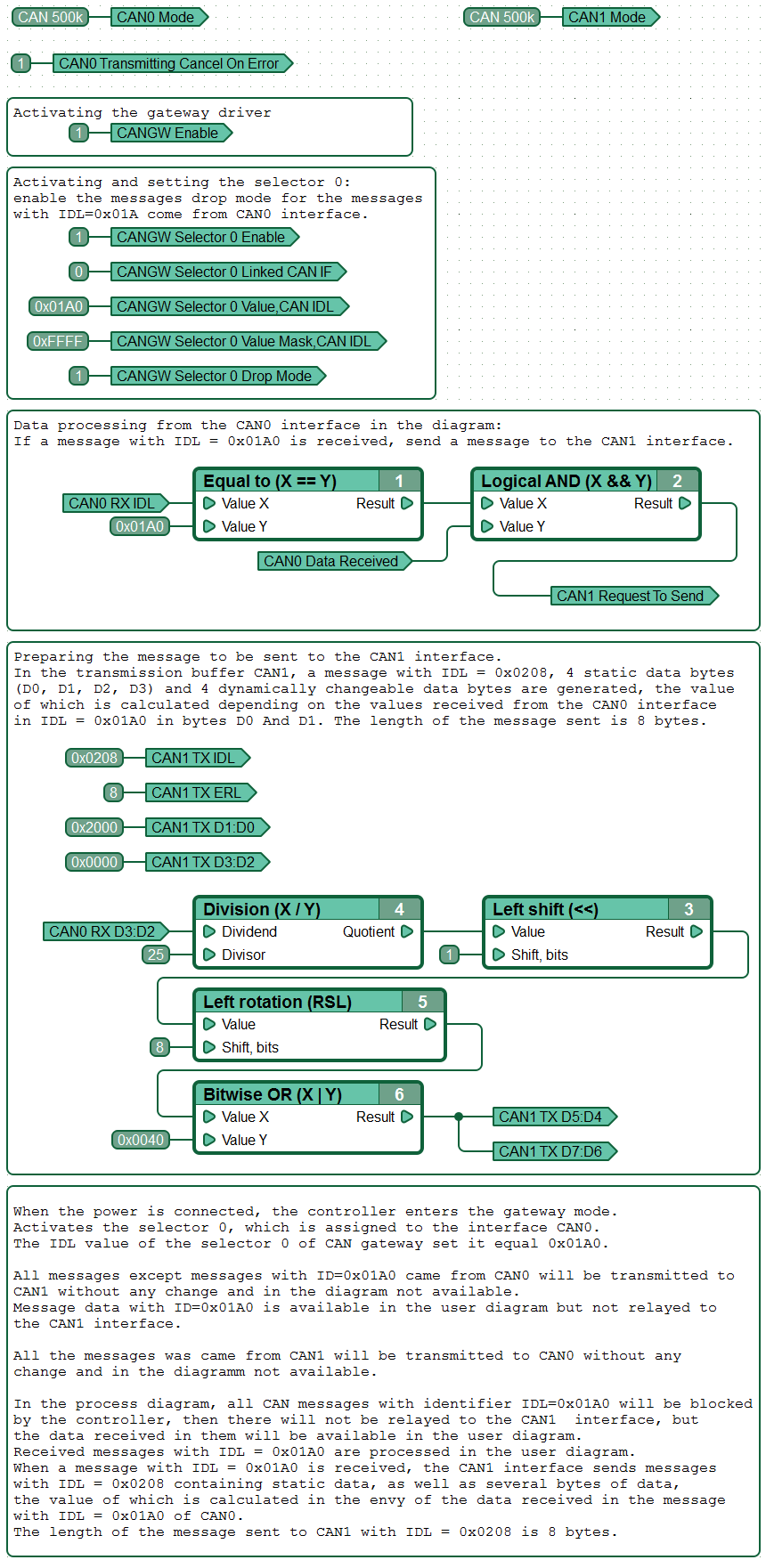
All messages, except messages with ID = 0x01A0, that come from the CAN0 interface are transmitted to CAN1 without any changes and are not included in the diagram. Message data with ID = 0x01A0 is available to the function diagram, but not relayed to the CAN1 interface.
All messages coming from CAN1 are transmitted to CAN0 without any changes and are not included in the diagram.
In the course of the diagram operation, all CAN messages from the CAN0 interface with IDL = 0x01A0 will be blocked by the controller. They will not be relayed to the CAN1 interface, but the data received from them will still be available to the function diagram.
Received messages with IDL = 0x01A0 are processed in the function diagram. When a message with IDL = 0x01A0 is received at the CAN1 interface, a message with IDL = 0x0208. The message contains static data, as well as several data bytes, the value of which is calculated depending on the data received in the message with IDL = 0x01A0. The length of the message sent to CAN1 with IDL = 0x0208 is 8 bytes.
Dynamic gateway
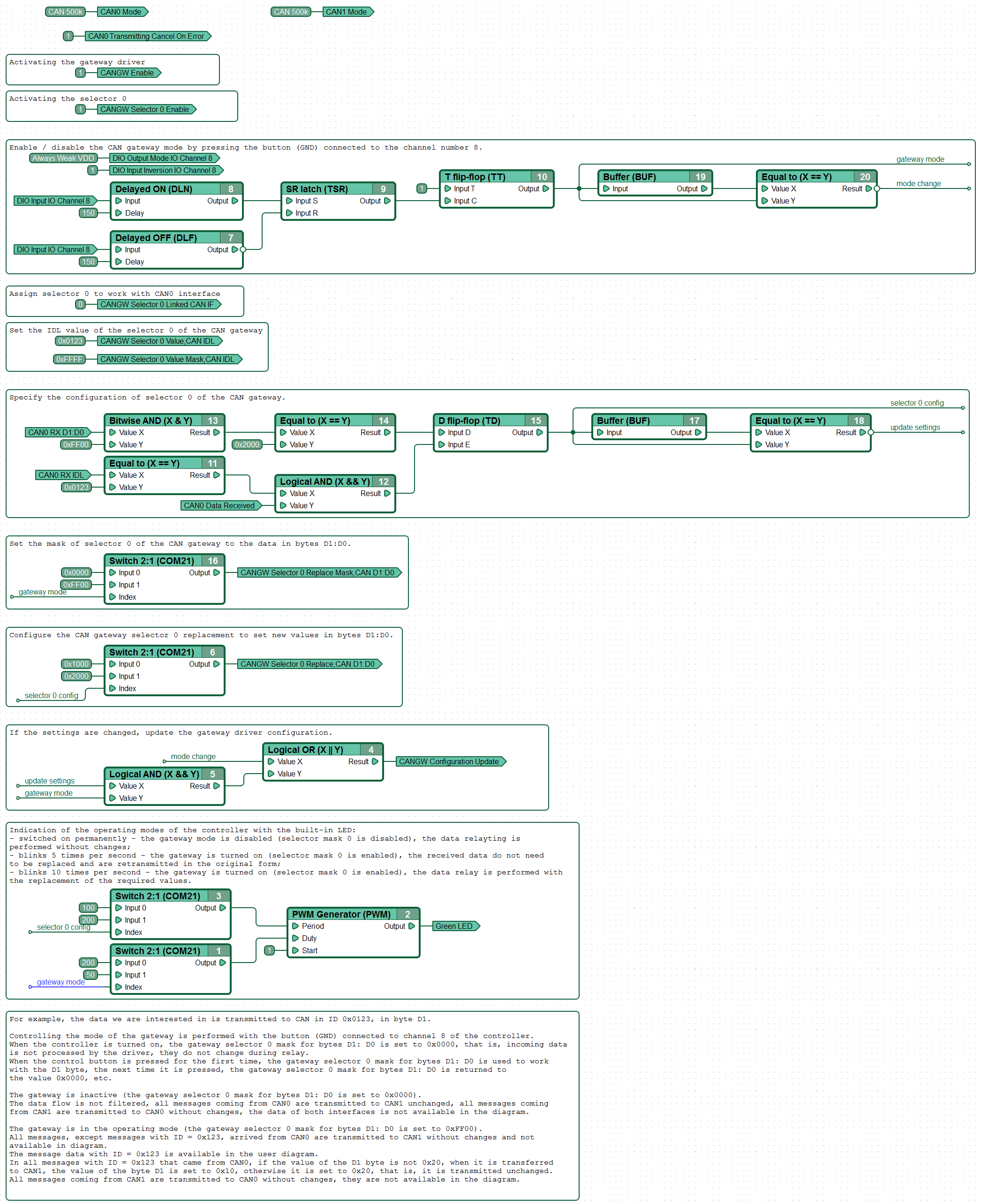
In this example, the data that is of interest to us is data byte D1 of messages transmitted to CAN with ID 0x0123.
The mode of operation of the gateway is controlled using a tactile switch (GND) connected to channel No. 8 of the controller. When the controller is turned on, the selection mask 0 of the gateway D1:D0 is set to 0x0000, i.e. the incoming data is not processed by the driver and is not modified during retransmission. The first time the control button is pressed, the selection mask 0 of the gateway D1:D0 is set to work with byte D1; the next time it is pressed, the selection mask 0 of the gateway D1:D0 is returned to the value 0x0000, etc.
When the gateway is inactive (selection screen 0 of gateway D1:D0 is set to 0x0000), data stream filtration is not performed, all messages that come from CAN0 are transmitted to CAN1 without any changes, all messages that come from CAN1 are transmitted to CAN0 without changes, the data of both interfaces are not included in the diagram.
When the gateway is active (selection screen 0 of the gateway D1:D0 is set to 0xFF00), all messages, except messages with ID = 0x123, that come from CAN0 are transmitted to CAN1 without any changes and are not included in the diagram. Message data of messages with ID = 0x123 is available in the function diagram. For all messages with ID = 0x123 sent from CAN0, if the value of byte D1 is not equal to 0x20, the value of byte D1 gets set to 0x10 when transmitting them to CAN1, otherwise the data gets relayed without any changes.
All messages coming from CAN1 are transmitted to CAN0 without changes and are not included in the diagram.
Attention! Any change in the settings of the gateway (for example, selection mask registers or selection replacement registers) requires updating the driver configuration using a special register.